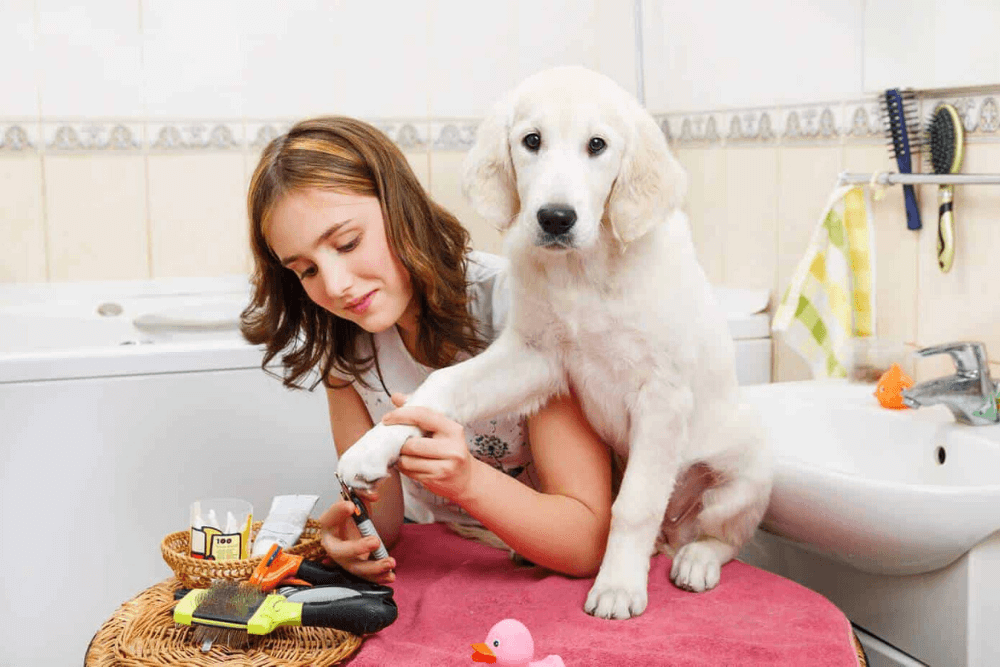
The relationship between humans and pets has evolved over thousands of years, transforming from wild animals to beloved companions. Understanding the evolution of pets provides insight into our deep connection with animals and the roles they play in our lives today. Here’s an overview of the historical journey of pet evolution.
1. The Origins of Domestication
Domestication of Dogs:
- Dogs are believed to be the first domesticated animals, with their origins tracing back to wolves. Genetic studies suggest that dogs were domesticated between 20,000 and 40,000 years ago.
- Early humans likely formed a mutually beneficial relationship with wolves, who helped with hunting and provided protection in exchange for food scraps.
Other Early Domestications:
- Following dogs, other animals began to be domesticated for various purposes. Cats were domesticated around 9,000 years ago, primarily for their ability to control rodent populations in agricultural settings.
2. Expansion of Pet Species
As human societies evolved, so did the variety of pets. The following animals became increasingly popular as companions:
- Cats: Revered for their hunting skills, cats transitioned from pest control to beloved household companions, especially in ancient civilizations like Egypt.
- Birds: Species like parrots and canaries became popular as pets for their beauty and ability to mimic sounds.
- Rodents: Hamsters, guinea pigs, and mice emerged as popular pets in the 19th and 20th centuries, particularly in urban areas.
- Reptiles and Exotic Animals: In recent decades, the trend has shifted to include reptiles (like snakes and lizards) and various exotic pets, reflecting changing attitudes towards animal companionship.
3. The Modern Pet Industry
With the evolution of pets has come the rise of the pet industry. Today, pets are often considered family members, leading to significant growth in services and products related to pet care:
- Healthcare: The veterinary industry has advanced dramatically, providing specialized care for various pet species.
- Nutrition: Pet food has evolved into a multi-billion-dollar industry, with specialized diets catering to the health needs of pets.
- Grooming and Boarding: Services such as pet grooming, daycare, and boarding facilities have become commonplace, offering convenience for pet owners.
- Technology: Innovations like pet tracking devices, smart feeders, and health monitoring apps have transformed how owners care for their pets.
4. Cultural Significance
Pets play a vital role in many cultures around the world, often symbolizing companionship, loyalty, and love. The ways in which pets are viewed and treated vary significantly across cultures:
- Companionship: In many Western cultures, pets are seen as companions that provide emotional support and joy.
- Working Animals: In other societies, certain breeds are still used for specific tasks, such as herding, guarding, or hunting.
- Status Symbols: In some cultures, owning specific breeds or exotic animals can be a status symbol, reflecting wealth and lifestyle.
5. Future Trends
As society continues to evolve, so will the relationship between humans and pets. Some emerging trends include:
- Increased Awareness of Animal Welfare: There is a growing focus on ethical treatment and adoption of pets, leading to more responsible ownership and care.
- Holistic Pet Care: More pet owners are seeking holistic approaches to pet health, including natural diets and alternative therapies.
- Technology Integration: The use of technology in pet care is expected to grow, with more innovations aimed at improving the quality of life for pets and ease of care for owners.
Conclusion
The evolution of pets reflects our changing relationship with animals and the significant roles they play in our lives. From ancient companions to modern family members, pets have adapted alongside humans, enriching our lives in countless ways. As we move forward, it’s essential to continue fostering responsible pet ownership and promoting the welfare of our animal companions.